This simple electronic circuit project has helped me out on many occasions. It is able to check transistors, in the circuit, down to 40 ohms across the collector-base or base-emitter junctions. It can also check the output power transistors on amplifier circuits.
Transistor Tester Circuit Diagram:
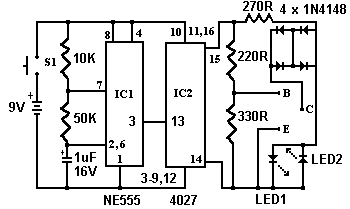
Circuit operation is as follows.
The 555 timer ( IC1 ) is set up as a 12hz multi vibrator. The output on pin 3 drives the 4027 flip-flop (IC2). This flip-flop divides the input frequency by two and delivers complementary voltage outputs to pin 15 and 14. The outputs are connected to LED1 and LED2 through the current limiting resistor R3. The LED's are arranged so that when the polarity across the circuit is one way only one LED will light and when the polarity reverses the other LED will light, therefore when no transistor is connected to the tester the LED's will alternately flash.
The IC2 outputs are also connected to resistors R4 and R5 with the junction of these two resistors connected to the base of the transistor being tested. With a good transistor connected to the tester, the transistor will turn on and produce a short across the LED pair. If a good NPN transistor is connected then LED1 will flash by itself and if a good PNP transistor is connected then LED2 will flash by itself. If the transistor is open both LED's will flash and if the transistor is shorted then neither LED will flash.
Comments
Post a Comment