The circuit consists of power supply and control sections. The power supply section is built around transformer X1, bridge rectifier BR1 and filter capacitor C1. The 50Hz, 230V AC mains is stepped down by transformer X1 to deliver a secondary output of 9V, 300 mA. The transformer output is rectified by the bridge rectifier and filtered by capacitor C1.
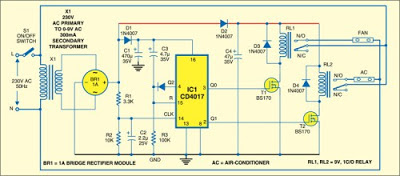
When the mains is switched on for the first time, pin 3 of IC CD4017 (IC1) goes high and relay RL1 energises to switch on the fan. When mains is briefly switched off using S1 and then switched on, the power to IC1 is maintained by the charge on capacitor C1. At the same time, there is a trigger pulse on the clock input (pin 14) of IC1, which advances the decade counter and relay RL2 energises to switch-on the air-conditioner. Both the air-conditioner and the fan will be turned off if the switch is in the ‘off’ position.
Assemble the circuit on a general-purpose PCB and enclose in a suitable case. Fix the unit onto the switchboard. Use relays RL1 and RL2 with proper contact ratings. The current rating depends on the load that you are going to control.
Assemble the circuit on a general-purpose PCB and enclose in a suitable case. Fix the unit onto the switchboard. Use relays RL1 and RL2 with proper contact ratings. The current rating depends on the load that you are going to control.
Author : D. N K
Comments
Post a Comment