Simple Mock Alarm with Call Bell Circuit Diagram is a fully automatic mock alarm to ward off any intruder to your house. The alarm becomes active at sunset and remains ‘on’ till morning. The flashing light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and beeps from the unit simulate the functioning of a sophisticated alarm system. Besides, the circuit turns on and off a lamp regularly at an interval of 30 minutes throughout the night. It also has a call bell facility.
The circuit is built around CMOS IC CD4060B (IC1), which has an internal oscillator and a 14-stage binary divider to provide a long delay without using a high-value resistor and capacitor.
Press switch S2 to provide 9V power supply to the circuit. During daytime, light-dependent resistor LDR1 offers little resistance and transistor T1 conducts. This drives transistor T2 into the cut-off mode, as its base is pulled to ground via transistor T1. Reset pin 12 of IC1 remains high as long as transistor T2 is cut off. This keeps the oscillator of IC1 (comprising resistors R5 and R6 and capacitor C1) disabled and its outputs remain low. The sensitivity of LDR1 can be adjusted using preset VR1.
Simple Mock Alarm with Call Bell Circuit Diagram
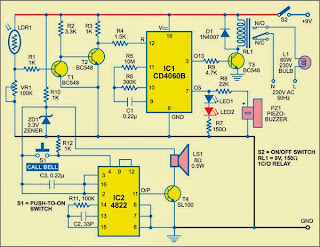
When the sunlight decreases in the evening, the resistance of LDR1 increases to cut off transistor T1. This drives transistor T2 into conduction mode and its collector voltage goes low. At the same time, reset pin 12 of IC1 goes low to enable the oscillator of IC1 and the oscillator starts oscillating. The O3 output (pin 7) of IC1 goes high every five seconds to light up the LEDs (LED1 and LED2) and activate the buzzer. Resistor R8 limits the tone produced from the buzzer.
At the same time, O13 output of IC1 (pin 3) goes high every 30 minutes to forward bias transistor T3 to energise relay RL1 and lamp L1 connected to the normally opened (N/O) contacts of relay RL1 glows. This cycle repeats till morning.
The call bell is built around IC 4822 (IC2). Its inbuilt musical tone generator generates different tones at each trigger. The frequency of the tone can be controlled through external components R11 and C2. The output at pin 11 of IC2 is amplified by transistor T4.
When push-to-on switch S1 is pressed once, trigger pin 4 of IC2 gets a positive trigger from the positive rail (reduced by zener diode to 3.3V) via resistor R10 and IC2 starts producing a melody. Resistor R10 limits the current to the trigger pin of IC2 and resistor R12 prevents any false triggering. Zener diode ZD1 provides the 3.3V required for IC 4822.
The circuit works off 9V regulated power supply. Assemble the circuit on any general-purpose PCB and enclose it in a waterproof plastic box with holes for mounting LEDs on the rear and the LDR on the top of the box. Place the LDR such that sunlight falls on it directly. Mount the unit on the pillar of the entrance gate. To avoid unnecessary illumination of the LDR, install lamp L1 away from the unit in the porch of the house. Keep the speaker inside the room.
Aothur D. Mohan Kumar and Thanx Streampowers
Comments
Post a Comment